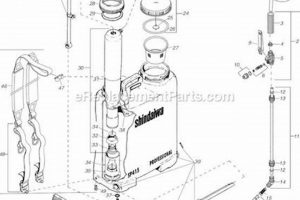
This equipment offers a portable solution for applying liquids, typically herbicides, pesticides, fertilizers, or cleaning solutions. It features a tank carried on the operator’s back via shoulder straps, coupled with a pump mechanism and a wand or nozzle for dispensing the fluid. Its design prioritizes user mobility and consistent application across varied terrains and extensive areas.
The value of such devices lies in their capacity to improve efficiency and precision in liquid application. The ergonomic backpack design reduces user fatigue compared to handheld sprayers, enabling extended operation. Furthermore, the ability to control spray patterns and flow rates minimizes waste and maximizes the effectiveness of the applied substance. Historically, these tools represent an evolution from less efficient manual spraying methods, addressing the growing demands of agriculture and landscaping for more sophisticated application technologies.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific models, features to consider when selecting this type of equipment, proper usage guidelines, and essential maintenance procedures. Detailed exploration of these topics will provide a comprehensive understanding of its operation and ensure optimal performance.
Operational Tips
Effective utilization of this equipment necessitates adherence to specific guidelines that ensure optimal performance and user safety. The following tips provide guidance on key operational aspects.
Tip 1: Pre-Operation Inspection: Prior to each use, thoroughly inspect all components, including the tank, hoses, wand, and nozzle. Ensure that all connections are secure and that there are no signs of leaks or damage. A damaged component can compromise performance and pose a safety hazard.
Tip 2: Proper Mixing Ratios: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended mixing ratios for the chemicals being used. Incorrect ratios can lead to ineffective application or damage to the target area. Accurate measurement tools are essential.
Tip 3: Consistent Pumping Technique: Maintain a consistent pumping rhythm to ensure a uniform spray pattern and flow rate. Avoid erratic pumping, which can result in uneven application. Practice smooth and deliberate strokes.
Tip 4: Appropriate Nozzle Selection: Select the appropriate nozzle for the specific application. Different nozzles produce varying spray patterns, such as fan, cone, or stream. Choosing the correct nozzle ensures targeted application and minimizes drift.
Tip 5: Wind Condition Awareness: Avoid spraying on windy days to prevent chemical drift. Drift can lead to unintended damage to non-target areas and pose a risk to the environment and human health. Monitor wind speed and direction before and during operation.
Tip 6: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, eye protection, and a respirator, when operating the equipment. PPE protects against chemical exposure and minimizes the risk of adverse health effects.
Tip 7: Post-Operation Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the equipment after each use. Rinse the tank, hoses, and nozzle with clean water to remove any residual chemicals. Proper cleaning prolongs the lifespan of the equipment and prevents cross-contamination.
Adherence to these operational tips maximizes the effectiveness of the equipment and minimizes the risk of accidents or environmental damage. Consistent application of these practices is crucial for responsible and efficient liquid application.
The subsequent section will address maintenance protocols for preserving the equipment’s operational integrity.
1. Capacity and Weight
The relationship between capacity and weight is a fundamental consideration in the selection and effective utilization of this equipment. These factors directly influence operator endurance, maneuverability, and overall productivity during spraying operations.
- Tank Volume Impact on Operational Time
A larger tank capacity allows for extended operation without the need for frequent refilling. However, a fully loaded tank significantly increases the overall weight of the unit, potentially leading to operator fatigue and reduced mobility, especially over uneven terrain or during prolonged use. For example, a model with a 4-gallon tank will require fewer refills than a 2-gallon model but will be considerably heavier when full.
- Empty Weight Influence on User Strain
The empty weight of the unit, independent of tank capacity, contributes to the overall burden placed on the operator. Lightweight materials and streamlined designs can minimize user strain, even before the tank is filled. A lighter initial weight is particularly advantageous for individuals of smaller stature or those with pre-existing physical limitations. For instance, polymer construction often results in a lighter unit compared to those made from metal components.
- Weight Distribution and Ergonomics
The distribution of weight across the operator’s back and shoulders is critical for comfort and stability. Ergonomic design features, such as padded shoulder straps, adjustable chest straps, and contoured back supports, help to distribute the load evenly, reducing pressure points and minimizing the risk of injury. An improperly balanced unit can lead to back pain and reduced control during operation.
- Material Density of the Tank
Tank Material plays a role in how much the unit will weigh. High-density polyethylene tanks are lighter than stainless steel. As a result the overall weight will be affected.
Balancing tank capacity and empty weight is crucial for optimizing user comfort and productivity. The ideal choice depends on the specific application, the operator’s physical capabilities, and the duration of the spraying task. Evaluating both factors ensures that the chosen equipment is both efficient and ergonomically sound.
2. Pump Mechanism
The pump mechanism forms the operational core of this equipment. It is the component responsible for generating the pressure required to deliver liquid from the tank, through the wand, and ultimately to the target area. A failure or inefficiency in this mechanism directly translates to inconsistent spray patterns, reduced flow rates, and diminished overall effectiveness of the spraying operation. For example, a malfunctioning diaphragm pump might result in pulsating or uneven spray, while a worn-out piston pump might exhibit a gradual decline in pressure output. The type of pump, whether manual or motorized, significantly influences the sprayer’s performance characteristics and user experience.
Different pump designs cater to varying application needs. Manual pumps, actuated by a lever or handle, offer simplicity and are typically found in smaller, less expensive units. They provide a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale applications. Motorized pumps, either battery-powered or gasoline-powered, provide automated pressure generation. Examples of its uses is a large agriculture setting. Their practical significance lies in enabling consistent spraying over extended periods, reducing operator fatigue, and delivering higher flow rates for larger areas. The choice of pump mechanism must align with the scale and demands of the intended spraying tasks.
Ultimately, the pump mechanism is an indispensable element of this equipment. Its reliability and performance directly impact the efficacy and efficiency of liquid application. Understanding the nuances of different pump types and their associated operational characteristics is essential for selecting the appropriate equipment and maintaining its performance over its lifespan. The pump mechanism will require regular inspection and maintenance, to prevent damage or degradation of the pressure regulator. Thus preventing the user or damage to property.
3. Nozzle Variety
The spectrum of nozzles available for this equipment plays a pivotal role in determining application precision and versatility. The selection of an appropriate nozzle directly impacts spray pattern, droplet size, and flow rate, thereby influencing the effectiveness of the applied substance and minimizing waste.
- Fan Nozzles: Broad Coverage Applications
Fan nozzles produce a flat, fan-shaped spray pattern, ideal for covering large, uniform surfaces such as lawns or fields. The consistent distribution ensures even application of herbicides or fertilizers. Conversely, their broad spray pattern can lead to increased drift in windy conditions, necessitating careful consideration of environmental factors.
- Cone Nozzles: Targeted Spraying and Penetration
Cone nozzles generate a conical spray pattern, creating smaller droplets that provide superior coverage and penetration, particularly within dense foliage. This nozzle type is well-suited for applying insecticides or fungicides to plants susceptible to pests or diseases. However, the finer spray may be more susceptible to evaporation in hot, dry climates.
- Adjustable Nozzles: Versatility and Adaptability
Adjustable nozzles offer the flexibility to modify spray patterns and flow rates, adapting to diverse application requirements. By simply twisting the nozzle head, the operator can switch between a stream for targeted applications and a cone or fan pattern for broader coverage. This versatility makes adjustable nozzles a practical choice for users with varied spraying needs.
- Specialty Nozzles: Precision and Control
Specialty nozzles, such as those designed for low-drift applications or foaming agents, address specific challenges or application requirements. Low-drift nozzles produce larger droplets, minimizing wind drift and reducing the risk of off-target contamination. Foaming nozzles create a visible foam layer, aiding in application tracking and ensuring complete coverage. These specialized options enhance precision and control in demanding environments.
The availability of diverse nozzle options empowers users to tailor the spraying operation to the specific demands of the task. The proper nozzle selection optimizes application efficiency, minimizes waste, and ensures the intended effect of the applied substance. The choice of nozzle is an integral aspect of maximizing the utility of this equipment.
4. Ergonomic Design
Ergonomic design constitutes a critical consideration in the engineering of these backpack sprayers, directly influencing user comfort, safety, and operational efficiency. A sprayer’s design significantly impacts the physical strain experienced during prolonged use. Thus, ergonomic principles are central to minimizing fatigue and maximizing productivity.
- Padded Shoulder Straps and Hip Belts
Padded shoulder straps distribute the weight of the sprayer evenly across the shoulders, preventing concentrated pressure points. Adjustable hip belts transfer a portion of the load to the hips, relieving strain on the back and shoulders. For example, wider, more contoured straps made of breathable materials can significantly reduce discomfort during extended operation. These features enhance user comfort and enable longer periods of use without excessive fatigue.
- Adjustable Frame Height
Adjustable frame heights allow the sprayer to be customized to the torso length of the operator. A properly fitted frame ensures that the weight of the sprayer is distributed correctly and that the center of gravity is aligned with the operator’s body. Failure to adjust the frame height can result in improper weight distribution, leading to back pain and reduced stability. A shorter individual would set the frame to a lower height to avoid the tank pressing against the back of the head.
- Contoured Back Support
Contoured back supports conform to the natural curvature of the spine, providing lumbar support and promoting proper posture. A well-designed back support minimizes strain on the lower back muscles, reducing the risk of back pain and injury. For instance, a molded foam back panel with ventilation channels can improve airflow and reduce sweating, further enhancing comfort.
- Handle and Wand Design
The design of the handle and wand impacts grip comfort, control, and reach. Ergonomically designed handles with textured surfaces reduce hand fatigue and improve grip, especially when wearing gloves. Lightweight wands with adjustable nozzles allow for precise application and reduce strain on the arms and wrists. Examples include curved wands for reaching under foliage and telescoping wands for extended reach.
These ergonomic features collectively contribute to a more comfortable and efficient spraying experience. By minimizing physical strain and promoting proper posture, ergonomic design enhances user safety, productivity, and overall satisfaction with this equipment. The integration of such design elements is paramount for maximizing the practical utility of these devices.
5. Material Durability
Material durability is a primary determinant of the lifespan and operational reliability of this equipment. The substances used in the construction of its various components dictate its resistance to wear, chemical degradation, and physical stress, thereby directly impacting its longevity and the total cost of ownership.
- Tank Material and Chemical Resistance
The tank, responsible for containing potentially corrosive chemicals, must exhibit high resistance to degradation. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a common choice due to its chemical inertness and impact resistance. However, prolonged exposure to certain solvents or concentrated chemicals can still lead to embrittlement or cracking. Stainless steel tanks offer superior chemical resistance but are heavier and more expensive. Selecting a tank material compatible with the intended range of chemicals is paramount.
- Hose and Seal Composition
Hoses and seals, which are consistently in contact with the sprayed liquids, are similarly susceptible to chemical attack. Materials like Viton or Teflon provide excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, preventing leaks and maintaining consistent flow. Inferior materials may degrade, leading to leaks, pressure loss, and eventual failure of the sprayer. Periodic inspection and replacement of hoses and seals are essential maintenance practices.
- Frame and Structural Components
The frame, responsible for supporting the tank and distributing its weight, must withstand mechanical stress and environmental exposure. Powder-coated steel or reinforced polymers offer a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and weight. Exposure to moisture and harsh chemicals can lead to rust or degradation, compromising the structural integrity of the sprayer. Regular cleaning and protective coatings can prolong the life of these components.
- Nozzle Construction and Wear Resistance
The nozzle, responsible for generating the spray pattern, is subject to wear from abrasive chemicals and physical impact. Hardened stainless steel or ceramic nozzles offer superior wear resistance compared to plastic alternatives. Clogged or worn nozzles result in uneven spray patterns and reduced application efficiency. Regular cleaning and replacement are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
The durability of materials employed in the construction of this equipment directly influences its long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. Selecting models with robust, chemically resistant materials and adhering to recommended maintenance practices are essential for maximizing the lifespan and reliability of these essential tools.
6. Maintenance Schedule
A carefully structured maintenance schedule is vital for preserving the operational effectiveness and extending the lifespan of a Stihl backpack sprayer. This schedule acts as a preventative measure against component failure and performance degradation. Without consistent maintenance, the sprayers output can become uneven, leaks can develop, and critical parts may prematurely wear out, leading to costly repairs or replacements. For instance, a neglected pump can lose pressure over time, requiring more effort from the operator to achieve the same level of spray coverage.
The maintenance schedule should encompass several key areas: regular cleaning after each use to prevent chemical buildup, periodic inspection of hoses and seals for cracks or leaks, and lubrication of moving parts to ensure smooth operation. Specific attention must be given to the nozzle, which can become clogged, altering the spray pattern. For example, the accumulation of dried chemicals in the nozzle can disrupt the uniformity of the spray, resulting in inconsistent application. Moreover, neglecting filter cleaning can obstruct the flow of liquid, reducing the sprayer’s overall efficiency.
In conclusion, adherence to a well-defined maintenance schedule is not merely a recommended practice but a necessity for ensuring the consistent and reliable performance of a Stihl backpack sprayer. Overlooking this aspect can lead to increased operational costs and reduced effectiveness. Therefore, integrating a proactive maintenance routine is essential for maximizing the long-term value and utility of this equipment.
7. Safety Features
The integration of safety features within the design and operation of this equipment is paramount, directly impacting operator well-being and minimizing the risk of accidents or chemical exposure. These features serve as critical safeguards, mitigating potential hazards associated with handling and applying potentially harmful substances. Without them, the risks of chemical burns, inhalation hazards, and environmental contamination increase substantially. An example is the inclusion of a check valve within the pump mechanism which prevents liquid from flowing back into the tank and potentially causing spills during refilling.
Specific safety features commonly incorporated into the design of this equipment include pressure relief valves, which prevent over-pressurization of the tank, and sealed compartments to protect the user from direct contact with chemicals. A trigger lock on the spray wand prevents accidental discharge, particularly important when transporting the equipment. Appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, eye protection, and respirators, are essential supplementary safety measures. A common scenario involves the use of a face shield to prevent chemical splashes from contacting the eyes during application.
The effective implementation and consistent utilization of these safety features are essential for responsible operation. Regular inspection of safety devices, proper training on their use, and strict adherence to safety protocols minimize the likelihood of incidents. The presence of safety features alone does not guarantee safety; operator awareness and responsible behavior are equally critical. By prioritizing safety, users can effectively harness the capabilities of this equipment while minimizing potential risks. The long-term benefits are less work related injury or sickness due to prolonged exposure or misuse of the equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding this equipment, providing concise answers to ensure informed usage and maintenance.
Question 1: What is the appropriate mixing ratio for herbicides used in this equipment?
The mixing ratio is dependent on the specific herbicide and target pest. Always consult the herbicide manufacturer’s label for precise instructions. Deviations from the recommended ratio can result in ineffective pest control or damage to desired vegetation. Adherence to label instructions is paramount.
Question 2: How often should the nozzle be cleaned to maintain optimal spray performance?
The nozzle requires cleaning after each use to prevent clogging from residual chemicals. Disassemble the nozzle components and rinse thoroughly with water. For persistent clogs, a soft brush or needle can be employed. Neglecting this cleaning can lead to uneven spray patterns and reduced efficiency.
Question 3: What is the recommended storage procedure for this equipment during the off-season?
Prior to storage, the tank must be completely emptied and rinsed. Thoroughly clean all components, including the hoses and nozzle. Store the unit in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This prevents degradation of plastic and rubber parts and ensures readiness for future use.
Question 4: What type of personal protective equipment (PPE) is necessary when operating this equipment?
Minimum PPE requirements include chemical-resistant gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and a respirator suitable for the chemicals being applied. Long sleeves and pants are also recommended to minimize skin exposure. The selection of appropriate PPE mitigates the risk of chemical exposure and associated health hazards.
Question 5: How can I prevent back strain when using this equipment for extended periods?
Ensure the sprayer is properly adjusted to fit the operator’s torso length. Utilize the padded shoulder straps and hip belt to distribute the weight evenly. Take frequent breaks to rest and stretch the back muscles. Proper fit and posture minimize the risk of back strain and fatigue.
Question 6: What is the expected lifespan of this equipment under normal operating conditions?
The lifespan is dependent on usage frequency, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. With proper care and adherence to the recommended maintenance schedule, a quality unit can provide several years of reliable service. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn components are crucial for extending its useful life.
These FAQs offer a foundation for understanding key aspects of usage and maintenance. Consulting the manufacturer’s manual remains essential for comprehensive information.
The next section will address troubleshooting common issues encountered during operation.
Conclusion
The preceding sections have comprehensively explored facets of equipment, ranging from operational guidelines and maintenance protocols to ergonomic design considerations and safety features. The objective has been to provide a thorough understanding of the device’s capabilities, limitations, and best practices for utilization.
Effective and responsible employment of equipment necessitates continuous adherence to safety protocols and a commitment to consistent maintenance. By embracing these principles, users can optimize its performance, extend its operational lifespan, and mitigate potential risks, thereby maximizing its value and contribution to intended applications. The user must be proactive and always prioritize safety, reading all instructions before utilizing. A continuous education is encouraged to keep up with regulatory and environmental changes for responsible use.