These specialized carrying solutions, designed for tactical and outdoor applications, are engineered to withstand demanding conditions. Constructed from durable materials such as Cordura nylon, they offer robust resistance to abrasion, tears, and water exposure. Features often include modular attachment systems, reinforced stitching, and specialized compartments for organizing and securing essential gear.
The adoption of such equipment provides users with enhanced organizational capabilities, increased carrying capacity, and improved load distribution, thereby minimizing strain and maximizing efficiency during extended operations. Historically, similar designs have been utilized by military personnel and law enforcement agencies to transport mission-critical supplies. The evolution of these designs reflects an increasing emphasis on ergonomic considerations and user-specific customization.
The subsequent sections will delve into a detailed examination of material properties, design elements, carrying capacity considerations, available features, and key selection criteria for tactical and outdoor backpacks. This comprehensive analysis aims to provide readers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding their specific needs.
Selection and Utilization Guidance
The following guidelines provide insights into selecting and effectively using tactical and outdoor carrying systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Tip 1: Material Assessment: Prioritize models constructed from high-tenacity nylon or similar abrasion-resistant fabrics. Verify the denier rating, with higher numbers indicating increased durability. For example, a 500D Cordura nylon offers a balance of weight and resistance to wear, suitable for most applications.
Tip 2: Stitching Integrity: Examine stitching patterns and reinforcement at stress points such as shoulder strap attachments and zippers. Double or triple stitching enhances structural integrity and prevents premature failure under heavy loads.
Tip 3: Load Distribution: Ensure the chosen model incorporates a robust suspension system with adjustable shoulder straps, sternum strap, and waist belt. Proper load distribution minimizes strain on the back and shoulders, improving comfort during extended use.
Tip 4: Compartmentalization: Evaluate the internal organization and the availability of specialized compartments. Dedicated pockets for hydration systems, electronic devices, and first-aid kits promote efficient access and prevent damage to sensitive equipment.
Tip 5: Environmental Considerations: Select a system with water-resistant or waterproof properties, particularly for use in inclement weather. A durable water repellent (DWR) coating or included rain cover provides added protection against moisture.
Tip 6: Modular Attachment: Consider models with modular attachment systems like MOLLE (Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment). This allows for the integration of additional pouches and accessories, expanding carrying capacity and customizing the configuration to specific mission requirements.
Tip 7: Zipper Quality: Evaluate the quality of zippers, opting for robust YKK zippers or similar reputable brands. Ensure smooth operation and resistance to jamming, even under stress.
Adherence to these guidelines will contribute to the optimal selection and utilization of carrying systems, maximizing their performance and extending their service life.
The concluding section will summarize the key considerations for making an informed purchase decision.
1. Durability
The durability of specialized load-bearing systems is paramount, dictating operational effectiveness and longevity. The materials employed, such as high-denier nylon fabrics, directly impact the ability to withstand abrasion, tearing, and puncture, particularly in demanding environments. Reinforced stitching at stress points, including strap attachments and zipper junctions, further contributes to structural integrity. Failure of a pack due to material weakness can compromise mission objectives and endanger personnel, necessitating stringent quality control in manufacturing processes.
For example, consider a scenario where military personnel rely on such a system to carry essential supplies during a multi-day operation in rugged terrain. If the pack fails due to inferior materials or construction, the loss of critical equipment can impede the mission. Similarly, search and rescue teams depend on the reliability of their equipment when navigating hazardous environments. The use of water-resistant coatings and reinforced bottom panels protects contents from exposure to the elements, preventing equipment malfunction and ensuring continued operational capacity. This emphasis on robust construction reduces the likelihood of needing replacements, promoting long-term cost-effectiveness and minimizing environmental impact.
In summary, a focus on durability within specialized load-bearing systems serves as a foundational element in mission success. By prioritizing high-quality materials, reinforced construction, and rigorous testing protocols, manufacturers enhance reliability, reduce risk, and ensure that these systems can withstand the challenges posed by demanding operational environments. Understanding this crucial element facilitates informed decision-making in selecting appropriate systems for specific applications.
2. Ergonomics
Ergonomics is a crucial consideration in the design and utilization of specialized load-bearing systems. The effectiveness of such systems hinges not solely on their carrying capacity, but also on their ability to distribute weight efficiently and minimize strain on the user. This directly impacts operational endurance and reduces the risk of injury.
- Adjustable Suspension Systems
A primary facet of ergonomic design involves adjustable suspension systems. These systems typically incorporate adjustable shoulder straps, sternum straps, and waist belts, enabling the user to customize the fit of the pack to their individual body dimensions and load requirements. Proper adjustment ensures weight is distributed across the skeletal structure, reducing pressure points and minimizing muscle fatigue. Improper adjustment can lead to back pain, shoulder strain, and reduced mobility.
- Load Distribution Frameworks
Internal or external frames are often integrated to facilitate efficient load distribution. These frameworks, typically constructed from lightweight materials such as aluminum or composite plastics, provide structural support and prevent the pack from deforming under heavy loads. By maintaining a stable center of gravity, these frameworks minimize the amount of energy required to maintain balance, thus increasing operational efficiency and reducing the risk of falls.
- Contoured Padding and Ventilation
Ergonomic designs incorporate strategically placed padding on contact points, such as shoulder straps and hip belts, to reduce friction and pressure. Contoured padding conforms to the user’s body shape, minimizing chafing and discomfort. Furthermore, ventilation channels promote airflow, reducing perspiration and maintaining a comfortable temperature during prolonged use. Lack of proper padding and ventilation can lead to skin irritation, discomfort, and decreased performance.
- Dynamic Load Transfer
Advanced designs employ dynamic load transfer mechanisms that allow the pack to move with the user’s body, minimizing resistance and maintaining a natural range of motion. This is particularly important in tactical scenarios where agility and maneuverability are paramount. Systems that restrict movement or create excessive friction can impede performance and increase the risk of injury.
The integration of these ergonomic principles into the design of carrying systems directly impacts user performance and safety. By optimizing load distribution, minimizing friction, and promoting natural movement, these design elements enhance operational effectiveness and reduce the likelihood of injury. The selection of a system with appropriate ergonomic features is a critical factor in ensuring long-term comfort and performance during demanding operations.
3. Organization
The inherent design of specialized load-bearing systems directly facilitates organized storage and retrieval of essential equipment. These systems incorporate a multitude of compartments, pouches, and attachment points, each serving a distinct organizational purpose. The effect of this design is enhanced operational efficiency, allowing users to rapidly access necessary items without extensive searching. A well-organized system minimizes time spent locating gear, crucial in time-sensitive scenarios. For example, medical personnel may require immediate access to first-aid supplies, while law enforcement officers need quick access to ammunition and communication devices. The ability to locate and deploy equipment rapidly can directly influence mission outcomes.
Furthermore, the implementation of modular attachment systems, such as MOLLE (Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment), enables users to customize the configuration of their carrying system according to specific mission requirements. Pouches and accessories can be added or removed, allowing for tailored organization of equipment. Consider a scenario where a tactical operator needs to carry specialized tools for a specific task. A MOLLE-compatible system allows the operator to attach pouches designed for those tools, ensuring they are readily accessible. This level of customization is not achievable with generic carrying solutions. The use of color-coded pouches and labeling systems further enhances organization, providing visual cues for rapid identification of contents.
In conclusion, organization is a foundational element of tactical and outdoor carrying systems, directly influencing operational efficiency and effectiveness. The presence of dedicated compartments, modular attachment systems, and user-configurable layouts enables efficient storage, retrieval, and deployment of essential equipment. Challenges in maintaining organization arise from the diverse range of equipment users must carry. However, the benefits of a well-organized system, including reduced search time and increased operational readiness, outweigh the challenges. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of organizational principles is vital when selecting and utilizing specialized carrying solutions.
4. Modularity
Modularity, within the context of specialized carrying systems, refers to the capacity for customization and adaptation through the addition or removal of components. This adaptability enhances the versatility of these systems, enabling them to meet diverse operational requirements. The integration of modularity principles directly impacts the functionality and utility of equipment.
- MOLLE (Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment) Integration
MOLLE compatibility represents a primary facet of modularity. This standardized system utilizes webbing to create attachment points for pouches and accessories, allowing users to configure the system to meet specific mission needs. A medic, for example, can attach specialized medical pouches, while a rifleman can add ammunition carriers. The absence of MOLLE limits customization, potentially hindering operational effectiveness.
- Interchangeable Components
Some designs feature interchangeable components, such as removable shoulder straps or waist belts, allowing users to adapt the system to different body types or load configurations. An individual might swap a padded hip belt for a minimalist strap to reduce weight during reconnaissance. This adaptability improves comfort and efficiency, particularly during extended operations.
- Customizable Internal Organization
Modularity extends to internal organization through adjustable dividers and removable compartments. Users can tailor the internal layout to accommodate specific equipment profiles, ensuring efficient storage and rapid access. A photographer might utilize padded dividers to protect lenses, while a technician could employ organizational panels for tools and electronics.
- External Attachment Points
Beyond MOLLE, external attachment points, such as compression straps and daisy chains, provide additional options for securing equipment. These features enable the attachment of bulky items, such as sleeping bags or trekking poles, that may not fit within the main compartment. A mountaineer, for example, might utilize these points to secure ice axes or crampons.
The modularity inherent in these systems enhances their adaptability, enabling users to tailor the system to specific mission requirements. This adaptability directly contributes to operational effectiveness and user satisfaction by ensuring equipment is readily accessible and properly configured for the task at hand. These modular designs offer a distinct advantage over static, non-customizable carrying solutions, solidifying their utility in diverse operational contexts.
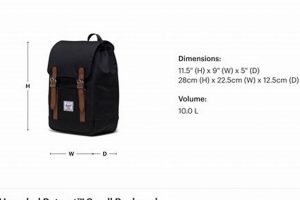
5. Capacity
Carrying capacity is a critical determinant in the selection and utilization of tactical carrying systems. The designated volume directly influences mission duration, equipment load, and overall operational effectiveness. Tasmanian Tiger backpacks offer a range of capacity options to suit various needs, requiring careful consideration of intended applications.
- Mission Duration and Load
Short-duration missions necessitate smaller-capacity packs, typically ranging from 20 to 30 liters. These packs accommodate essential items such as water, rations, and basic first-aid supplies. Extended operations demand larger capacities, potentially exceeding 50 liters, to accommodate additional equipment like sleeping bags, extra clothing, and specialized tools. For example, a reconnaissance patrol operating for 24 hours may utilize a smaller pack, while a multi-day expedition requires a larger volume for sustenance and shelter.
- Equipment Type and Volume
The type of equipment carried directly influences capacity requirements. Bulky items, such as communication devices or specialized medical equipment, necessitate larger packs. Conversely, missions requiring minimal equipment can utilize smaller, more streamlined designs. An emergency medical technician (EMT) responding to a disaster may require a larger capacity to accommodate oxygen tanks and advanced medical supplies, whereas a law enforcement officer on patrol may require a smaller pack for basic gear.
- User Physical Attributes
Individual physical attributes, including torso length and body mass, impact the suitability of different pack sizes. A smaller individual may find a large-capacity pack unwieldy and difficult to manage, while a larger individual may require a larger pack to comfortably distribute the load. Ergonomic considerations are paramount; a properly sized pack enhances comfort and minimizes the risk of injury. A shorter person utilizing a pack designed for a taller individual may experience discomfort and reduced mobility.
- Weight Distribution and Stability
Capacity directly affects weight distribution and overall stability. Overloading a pack can compromise stability and increase the risk of falls, particularly in uneven terrain. Proper weight distribution, with heavier items positioned closer to the user’s center of gravity, enhances balance and reduces strain. A poorly distributed load can lead to muscle fatigue and potential injury. Maintaining appropriate load discipline is crucial for long-term operational effectiveness.
The relationship between capacity and mission parameters underscores the importance of selecting the appropriate Tasmanian Tiger backpack for a given application. Overestimation or underestimation of capacity requirements can negatively impact operational effectiveness and user safety. Careful consideration of mission duration, equipment load, user attributes, and weight distribution principles is essential for optimal performance.
6. Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is a critical performance attribute of tactical carrying systems. Exposure to precipitation, humidity, and extreme temperatures directly affects the integrity and functionality of carried equipment. A lack of adequate weather protection can lead to equipment malfunction, corrosion, and degradation of essential supplies. Therefore, weather resistance is a paramount consideration in the design and material selection of carrying systems intended for use in diverse environments. The implications of failing to protect equipment from the elements can range from minor inconvenience to mission failure, depending on the severity of the conditions and the sensitivity of the carried items.
The implementation of weather-resistant features in tactical backpacks involves several key design elements. Durable water repellent (DWR) coatings are commonly applied to outer fabrics to repel water and prevent saturation. Waterproof or water-resistant zippers and sealed seams further minimize water ingress. Some systems incorporate integrated rain covers that can be deployed in heavy precipitation. Material selection also plays a crucial role; high-denier nylon fabrics with inherent water resistance properties are favored. The effectiveness of these measures is directly proportional to the level of protection provided. For instance, an electronic device exposed to moisture can become inoperable, compromising communication capabilities, navigation systems, and data collection efforts. Similarly, saturated clothing can lead to hypothermia, reducing operational effectiveness and posing a health risk.
Weather resistance is not merely a desirable feature but a necessity for specialized carrying systems intended for use in demanding environments. The implementation of appropriate design elements and material selection is essential to ensure the integrity and functionality of carried equipment, contributing to operational effectiveness and user safety. The absence of adequate weather protection can have significant and potentially mission-compromising consequences. Therefore, evaluating weather resistance is a critical step in selecting a suitable carrying system for specific operational requirements. This aspect ensures the reliability and longevity of the system, solidifying its utility in diverse environmental conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tasmanian Tiger Backpacks
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, use, and maintenance of specialized load-bearing equipment.
Question 1: What factors determine the appropriate carrying capacity for a Tasmanian Tiger backpack?
Carrying capacity is determined by mission duration, equipment volume, and user physique. Longer operations and larger equipment loads necessitate greater capacity. Ergonomic considerations also dictate appropriate size.
Question 2: How does the denier rating of nylon fabric impact the durability of these backpacks?
The denier rating indicates fabric weight and thickness. Higher denier values correlate with increased abrasion resistance and overall durability, enhancing the backpack’s lifespan.
Question 3: What are the benefits of a MOLLE (Modular Lightweight Load-carrying Equipment) system?
A MOLLE system enables customization through the attachment of pouches and accessories, tailoring the backpack’s configuration to specific mission requirements. This modularity enhances adaptability.
Question 4: How should a Tasmanian Tiger backpack be adjusted to ensure proper weight distribution?
Adjust shoulder straps, sternum strap, and waist belt to distribute weight across the skeletal structure. Position heavier items closer to the center of gravity to enhance balance and reduce strain.
Question 5: What maintenance procedures are recommended for preserving weather resistance?
Regular cleaning removes dirt and debris that can compromise water repellency. Reapply DWR (durable water repellent) coatings periodically to maintain weather resistance. Store the backpack in a dry environment.
Question 6: How does ergonomic design contribute to user performance and safety?
Ergonomic design, including contoured padding and adjustable straps, minimizes strain, improves comfort, and promotes natural movement. These elements enhance operational effectiveness and reduce the risk of injury.
These FAQs provide critical insights for maximizing the functionality and longevity of load-bearing systems.
The concluding section will provide a summary of key considerations for the user.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored core attributes of Tasmanian Tiger backpacks, emphasizing durability, ergonomics, organization, modularity, capacity, and weather resistance. These factors are fundamental in determining the suitability of such systems for tactical and outdoor applications. A comprehensive understanding of these elements enables informed decision-making when selecting equipment to meet specific operational needs.
The strategic implementation of appropriately chosen carrying systems can significantly enhance mission effectiveness and user safety. Continued innovation in design and materials will further optimize the performance of these systems, solidifying their critical role in diverse operational contexts. Therefore, ongoing evaluation and adaptation remain essential to maximize the benefits derived from these tools.